
In this article:
Asset Management Standard ICML 55
Responsibilities of an MLE
Skills and Knowledge
Routine Tasks of an MLE
I’m proud to say that the Machinery Lubrication Engineer (MLE) certification has become a reality. Through studying and testing, qualified candidates can earn the right to hold this prestigious title, and Noria has developed a training course to help students prepare. Unlike other exams and certifications related to lubrication and lubricant analysis, the MLE stands alone as the highest professional designation in our industry. It also has a more holistic purpose. Let me explain.
Many know that the International Council for Machinery Lubrication (ICML) was organized to serve practitioners in the lubrication field, especially maintainers of lubricated mechanical machinery. So, it makes sense that the MLE would have a similar focus and purpose.
Perhaps the best way to describe the profile of those whom the ICML targets for MLE certification is to look at the 35 subject-matter experts and volunteers who toiled for years to bring it to life. These individuals are the thought leaders and trusted advisors who have helped guide the ICML as well as the larger global lubrication community.
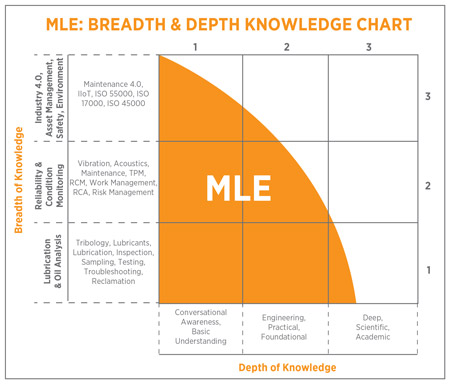
Figure 1. The breadth and depth
of knowledge to become certified as a Machinery Lubrication Engineer.
You might say they are “real-world” lubrication and reliability experts. Their knowledge is not limited to books, scientific research, mathematical models, tribology journals or formulation chemistry. Instead, they are hands-on professionals who practice in their field, who have learned more from experience than theory and who focus more on the practical than the abstract.
I mentioned holistic because the ICML committee assembled a body of knowledge (BoK) for the MLE that goes beyond traditional lubricant and lubrication subjects. Like other certifications, the MLE BoK consists of the topics that must be mastered to become certified. Yes, there is a need for solid competency related to lubricants and lubrication. What is not needed, though, is deep technical knowledge that falls outside the maintenance and reliability plant-environment workplace.
Furthermore, lubrication co-mingles with numerous companion reliability and asset management subjects. It should not be separated from the many tasks and functions that have shared objectives. A body of knowledge was needed that defined cross-functional skills and competencies to adequately serve the “big picture” in reliability and asset management. Likewise, it needed to project a comprehensive understanding of what lubrication is trying to achieve and how lubrication professionals enable the realization of these objectives through knowledge, competency and execution.
On the surface, this sounds easy. The reality was quite different. Deciding what to include and what not to include was a monumental task that took great vision and a fair bit of deliberation by volunteer experts. After all, without a consensus on the BoK, the construction of even the first MLE test question could not begin.
See Figure 1 for a chart illustrating the breadth and depth of knowledge to become certified as an MLE.
Enter Asset Management Standard ICML 55
The solution for scoping and completing the MLE body of knowledge was first to write an overarching standard on the management of lubricated mechanical assets. The main requirements of this standard (part 1) have now been written and are available through the ICML (see the announcement article by Paul Hiller).
It is the work-product of four years by 45 experts who possess broad knowledge on subjects both central and peripheral to the lubrication field. These include 34 trainers and consultants, nine book authors, 40 separate organizations and 15 countries. Most of these experts also participated in the formation of the MLE.
ICML 55.1 is the standard (part 1 of 3) that carefully delineates the requirements for certification. It is mapped structurally to ISO 55001, ISO 14001 and ISO 9001, which also address requirements for compliance and certification.
ICML 55.1 is organized across 12 subject areas, or elements, for how compliance can be achieved where life cycle and reliability needs must be optimized and balanced against maintenance resources. It will be followed soon by ICML 55.2, which is a practical guideline for asset owners on how to achieve compliance of the requirements listed in ICML 55.1.
ICML 55 is a seminal work in the field of lubrication and condition monitoring. As such, it has no precedence. It is the work of the global lubrication, tribology, reliability, condition monitoring and asset management community.
For the first time, definition and specificity are provided, clearly stating the practical and realistic meaning of lubrication excellence and its role in supporting reliability, safety, environmental responsibility, energy conservation, asset management and much more.
By following the requirements of ICML 55.1, users not only can achieve an optimized level of reliability but also can have the foundational bedrock for programmatic sustainability. Such sustainability is essential to counter shifting-ground challenges associated with aging machines, environmental issues, new technology (e.g., Industry 4.0), staffing/management changes, ownership changes, etc.
Any organization on an ICML 55 journey requires an individual with both technical and programmatic knowledge to blaze the trail in pursuit of full organizational certification. The MLE is that individual. The 24 subjects in the MLE body of knowledge were extracted directly from the 12 interrelated subject areas of ICML 55.1.
This perfect alignment is strategic and purposeful, engineered to facilitate achievement and sustainability of lubrication in the context of reliability, maintenance and asset management, as well as ICML 55.1 certification. Figure 2 lists the 12 ICML 55 subjects and includes a chart illustrating the stages of maturity on the journey to full compliance and certification.
Responsibilities of a Machinery Lubrication Engineer
An MLE is a professional with extensive training and experience. Certification validates competency. This individual may hold other certifications such as Certified Maintenance & Reliability Professional (CMRP), Machine Lubrication Technician (MLT), Machine Lubricant Analyst (MLA), Certified Lubrication Specialist (CLS) or Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE). Most MLEs will pursue a management path, but others may prefer more technical jobs like staff engineer, consultant or advisor. In a typical plant, the MLE likely will have task responsibility over technicians, analysts, inspectors, operators, millwrights and others performing a wide range of lubrication-related work.
Those interested in training with Noria to prepare for this certification have the option to train in a virtual classroom with Noria experts, through on-demand recordings,
An MLE is a professional with demonstrated competencies in the 24 body of knowledge subject areas. The complete BoK and domain of knowledge can be found at ICML Online.
Skills and Knowledge
Carefully read the MLE responsibilities listed below. The skills and knowledge needed to perform the jobs on the list are extensive and run deep. In an age of Industry 4.0, Maintenance 4.0, lean manufacturing and asset management, it would be foolhardy to view the responsibilities of the MLE as trivial or pedestrian.
The concept and definition of lubrication excellence have been rewritten and will continue to evolve. The bar has been raised and is held as the new standard of excellence. The MLE is a high distinction and is ready today.

Figure 2. The list of 12 ICML 55 subjects along with an illustration showing the stages of maturity for full compliance and certification.
Routine Tasks of a Machinery Lubrication Engineer
The following is a breakdown of the many routine jobs or tasks that may fall under the responsibility of a Machinery Lubrication Engineer. Of course, this will vary considerably from company to company.
Selection of Lubricants
- Oversees the selection and performance specifications of all lubricants
- Establishes grease vs. oil guidelines
- Ensures lubricants are optimally selected with respect to cost, reliability, energy conservation, safety, quality and environmental factors
- Ensures lubricants are compatible with the machine, process fluids and work environment
- Writes standards for all lubricant products
- Implements a lubricant consolidation strategy
- Is a member of the buying team for selection of lubricant supplier(s)
Selection of Lubrication Equipment
- Selects oil mist, single-point, centralized and other automatic lubrication equipment
- Selects oil level control devices
- Selects sight glasses and bottom sediment and water (BS&W) bowls
- Selects top-up and dispensing containers as well as fill port hardware
- Selects lubricant dispensing equipment
- Selects grease fittings, tags and grease guns
- Selects storage room tools and equipment
Selection of Contamination Control Products
- Defines fluid cleanliness and dryness targets
- Selects filter suppliers, filter types and performance specifications
- Verifies that lubricants and additives are compatible with filters and separators
- Selects breathers and headspace-management equipment
- Selects oil reclamation equipment and/or service providers
- Selects filter carts and offline filtration equipment
- Selects lubricant heaters and coolers
- Selects sump reservoir flushing and cleaning equipment and/or service providers
Management of Lubrication Suppliers and Service Providers
- Oversees quality, service and support by vendors for lubricants and related products and services
- Identifies procedures for receiving inspection of incoming products (including lubricants)
- Establishes lubrication and contamination control guidelines associated with equipment rebuilders
- Sets up a supplier performance tracking program
- Routinely communicates supplier performance to purchasing, engineering and management
Lubrication and Inspection PMs and Work Order Management
- Oversees the writing and scheduling of routine lubrication and inspection PMs, and ensures they are consistent with best practice
- Oversees staffing and performance of lubrication work orders
Writes Lubrication Procedures to Be Consistent with Best Practice
- Tank/sump flushing and cleaning
- Oil drain interval and criteria (interval based or condition based)
- Top-up procedures
- Grease gun calibration
- Handling and storage practices
- Machine inspections
- Contamination control
- Filter changes and used filter inspection
- Grease gun operation (including how much and how often)
Lubricant Handling, Storage, Consumption and Conservation
- Oversees all lubricant storage room activities and equipment, including layout, lube container selection, transfer equipment, pumps and tools, ventilation, funnels and hoses, safety equipment and procedures, housekeeping standards, training, record-keeping, etc.
- Responsible for management of lubricant inventories, reorder points, stock rotation, setting of expiration dates, product labeling and incoming delivery inspections
- Responsible for tracking and management of lubricant consumption, including leakage control
- Establishes lubricant consumption strategies
- Responsible for environmental conservation practices, including best practices for waste oil and used-filter disposal
Develops Lubrication-related Engineering Specifications for New Machinery
- Identification of all lubrication points, lubricant type, procedure and frequency of relubrication
- Installation of sampling ports and procedure
- Set up of oil analysis testing requirements by machine
- Filter, breather and vent selection
- Selection of level gauges, sight glasses and other inspection windows
- Flushing ports and quick-connect selection
- Initial cleanliness/dryness targets
- Training of lubrication technicians on proper PMs and inspections
- Participates in the commissioning of new equipment
Warranty and Regulatory Compliance Management
- Ensures machines are lubricated in accordance with manufacturer warranties
- Ensures warranty claims are submitted for defective lubricants and lubrication equipment
- Ensures all lubricants and lubrication practices (including storage, containment and disposal) are in compliance with relevant government regulations and industry standards
Manpower Planning, Administration, Staff Training and Certification
- Writes job descriptions, defines job skills and defines certification requirements for maintenance employees/contractors with lubrication responsibilities
- Manages all lubrication and oil analysis direct-line reports and job responsibilities
- Conducts quarterly skill-development workshops for lubrication technicians and analysts
- Selects and schedules onsite training programs, including certification relating to oil analysis, failure analysis, troubleshooting, lubrication best practices and contamination control
Lubrication Information Management
- Supports the selection and management of lubrication software and other information technology products/processes, including data entry, oil analysis software, predictive maintenance (PdM) software, lubrication scheduling software and related computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) modules
Oil Analysis Program Design and Coordination
- Selects the oil analysis laboratory
- Selects onsite oil analysis instruments
- Selects oil analysis software and report format
- Identifies when, how and where samples will be obtained
- Selects routine oil analysis test slate for each machine
- Sets oil analysis alarms and condemning limits
- Defines additive reconstruction strategies
- Performs/coordinates laboratory-quality assurance tests
- Provides data integration and interface to other reliability technology activities, including vibration, acoustics and thermography
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA); Failure Reporting, Analysis and Corrective Action System (FRACAS); Root Cause Analysis (RCA); and Troubleshooting
- Participates in FMEA and reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) planning initiatives
- Participates in RCA and FRACAS activities relating to failures of grease- or oil-lubricated machinery
- Develops troubleshooting templates and fault trees for common machine conditions and trains maintenance staff on their use
Management Reporting and Performance Metrics
- Defines overall lubrication program goals, budgets and plans
- Evaluates proposed lubrication capital expenditures using standard economic analysis methods
- Coordinates annual lubrication audits and benchmarking services
- Implements overall lubrication effectiveness metrics and other key performance indicators
- Makes routine progress reports to management and maintenance staff
- Ensures the overall lubrication activity program is aligned with asset management, reliability, safety and environmental objectives





_small.jpeg)



